XAT 2015 Quant & DI: Sum of AP
This question appeared as a part of the quantitative reasoning and data interpretation section of the XAT 2015. A total of 31 questions appeared in this section in XAT 2015. This question is a relatively very easy question and tests the concept of summation of an arithmetic sequence.
Question
What is the sum of the following series? -64, -66, -68, ..... , -100
- -1458
- -1558
- -1568
- -1664
- None of the above
Correct Answer Choice B. The sum is -1558.
Explanatory Answer
-
Step by step solution
The sequence is -64, -66, -68, ..... -100.
The given set of numbers are in an arithmetic progression.- Key Data: First term is -64. The common difference is -2. The last term is -100.
- Sum of the first n terms of an AP = \\frac{n} {2} [{2{a_1} + ({n - 1}) d}] \\)
To compute the sum, we know the first term a1 = -64 and the common difference d = -2.
We do not know the number of terms n. Let us first compute the number of terms and then find the sum of the terms. - Step to compute number of terms of the sequence
an = a1 + (n - 1)d
-100 = -64 + (n - 1)(-2)
Therefore, n = 19.
- Sum Sn = \\frac{19} {2} [{2({-64}) + ({19 - 1}) (-2)}] \\)
Sn = \\frac{19} {2} [{-128 -36}] \\)
Sn = 19 * (-82) = -1558
The correct answer is Choice B.
- Key Data: First term is -64. The common difference is -2. The last term is -100.
-
Alternative Method
The sum of any set of numbers = Average of the numbers * number of terms
- Step 1: Compute Average
Average of the terms of an arithmetic sequence = \\left[\frac{first \space term \space + \space last \space term} {2} \right]\\)
Average of this sequence = \\left[\frac{-64 \space -100} {2} \right]\\) = -82
- Step 2: Compute Sum Sum = Average * number of terms
We have computed the number of terms in the text book approach. Number of terms = 19.
Therefore, sum = (-82) * 19 = -1558
- Step 1: Compute Average
-
Formulae to remember in Arithmetic Sequence
An arithmetic progression is such a sequence in which every subsequent term of the sequence is obtained by adding the preceding term with a constant number. This constant number is called the common difference(d) of the sequence.
e.g., 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 is an arithmetic sequence.
The second term is obtained by adding the first term by 2. The third term is obtained by adding the second term by 2 and so on.Formula 1: nth term of a Arithmetic Progression an = a1 + (n - 1)d, where a is the first term of the sequence and d is the common difference.
Formula 2: Sum of the first n terms of a arithmetic progression =
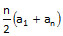
Alternatively, you can find the sum using this formula Sn =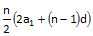
Video Explanation
More Questions on Arithmetic, Geometric Progression
- Find the sum of terms of a GP
- AP: find a term; sum known
- Sum of AP having -ve common difference
- AP: find a terms; sum & product given
- Sum of an AP Series
- CAT 2003: Find sum of terms of an AP
- AP: Integers divisible by 4 or 9
- TANCET 2013: Sum of a GP
- XAT 2014: AP & Divisibility
- XAT 2015: Sum of an AP
- Logarithm terms in an AP
- Speed Distance Time & AP
Online TANCET MBA Course
Try it Free!
Register in 2 easy steps and start learning in 5 minutes!
Already have an Account?
XAT TANCET Practice Questions - Listed Topic wise
- Number Theory
- Permutation Combination
- Probability
- Inequalities
- Geometry
- Coordinate Geometry
- Mensuration
- Trigonometry
- Data Sufficiency
- Percentages
- Profit Loss
- Ratio Proportion
- Mixtures & Alligation
- Speed Distance & Time
- Pipes, Cisterns & Work, Time
- Simple & Compound Interest
- Races
- Averages & Statistics
- Progressions : AP, GP & HP
- Set Theory
- Clocks Calendars
- Linear & Quadratic Equations
- Functions
- English Grammar
- General Awareness
